| Audio Dublikat Analyse unter zur Hilfenahme der Fast-Fourier-Transformation (FFT) | ||||||
| Verfahrensbeschreibung nach Kurt Rosenfeld's FDMF - [Beta-Stadium] | ||||||
| 1) Erzeuge eine Liste aller Musikdateien im Musikverzeichnis Für jede Datei: 2) Dekodiere und Dekomprimiere Datei in Roh-Binärdaten (raw 16-bit stereo native endian audio data) | ||||||
| 3) Berechne die enthaltene Energie (E=hf) in 4 Frequenzbändern (b0 3,b1 15,b2 90,b3 600,5000) für jeden 250ms-Zeitabschnitt in[i] b[0]=3 b[1]=15 b[2]=90 b[3]=600 b[4]=5000 | ||||||
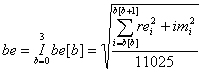 | ||||||
| 3.1) Berechne für jeden Zeitabschnitt die Summe der Energien der 4 Frequenzbänder 3.2) Berechne (b2 + b3):(b0 + b1) für jeden Zeitabschnitt 3.3) Berechne (b0 + b2):(b1 + b3) für jeden Zeitabschnitt 4) Berechne die spektrale Leistungsdichte der Schritte 3.1, 3.2, and 3.3 5) Spline fit power spectra to a fixed set of frequency points 6) Quantisiere das Ergebnis aus Schritt 5 auf ein Bit unter Verwendung des Medians als Schwellwert 6.1) Speichere das Ergebnis in einer Datenbank FOR EACH POSSIBLE PAIR OF FILES: 7) Count the number of bits that are the same in the two spectra. 8) If the result of 7 exceeds a threshold, and both files still exist, print the filenames. | ||||||
| fdmf keeps a cache of the results of step 6. This cache persists from one invocation of fdmf to the next in the form of a database file in the user's home directory. (~/.fdmf) If a music file has its step 6 result already in the cache, then step 2 through step 6 will be skipped for that file. That speeds things up by about two orders of magnitude. If a music file is identical (data has the same MD5 hash) to another file that has already been indexed, then the step 6 result will be copied from the existing index entry to the new index entry. This skips steps 2 through 6 and speeds up processing of that file by about two orders of magnitude. In the worst case (no identical files) this slows things down by about 1%. After finding that two files in the database seem to match, vector_pairs checks to make sure that both files exist. If they don't exist, it will suppress the output regarding that pair. The goal of this is to only print messages about actual duplicate files, but to keep the records for all files that have been analyzed. If sometime later you get the exact same file (based on MD5 sum) then fdmf will just reuse the summary that it already has. The summaries are small, so for most people, it is worth it to cache these "ghost" records. Steps 1 through 6.5 are implemented in fdmf. Steps 7 and 8 are implemented in vector_pairs in C. | ||||||
 fdmf-0.0.9s.tar.gz (Executable, 23 KB) fdmf-0.0.9s.tar.gz (Executable, 23 KB) | ||||||
 fdmf.0.0.9j.spec (Executable, 1 KB) fdmf.0.0.9j.spec (Executable, 1 KB) | ||||||
| Datei-Archiv | ||||||
 fdmf.spec (Executable, 1 KB) fdmf.spec (Executable, 1 KB) | ||||||
 fdmf-0.0.9r.tar.gz (Executable, 23 KB) fdmf-0.0.9r.tar.gz (Executable, 23 KB) | ||||||
 fdmf-0.0.9q.tar.gz (Executable, 23 KB) fdmf-0.0.9q.tar.gz (Executable, 23 KB) | ||||||
| ||||||
| ||||||
 top top | ||||||
| Provided by Hannes Migga-Vierke last modified 26 Jul 2010 | ||||||
 | Home |
 | ALF |
 | Futurama |
 | Technik-Ecke |
 | Archiv |
 | Links |
 | Impressum |







